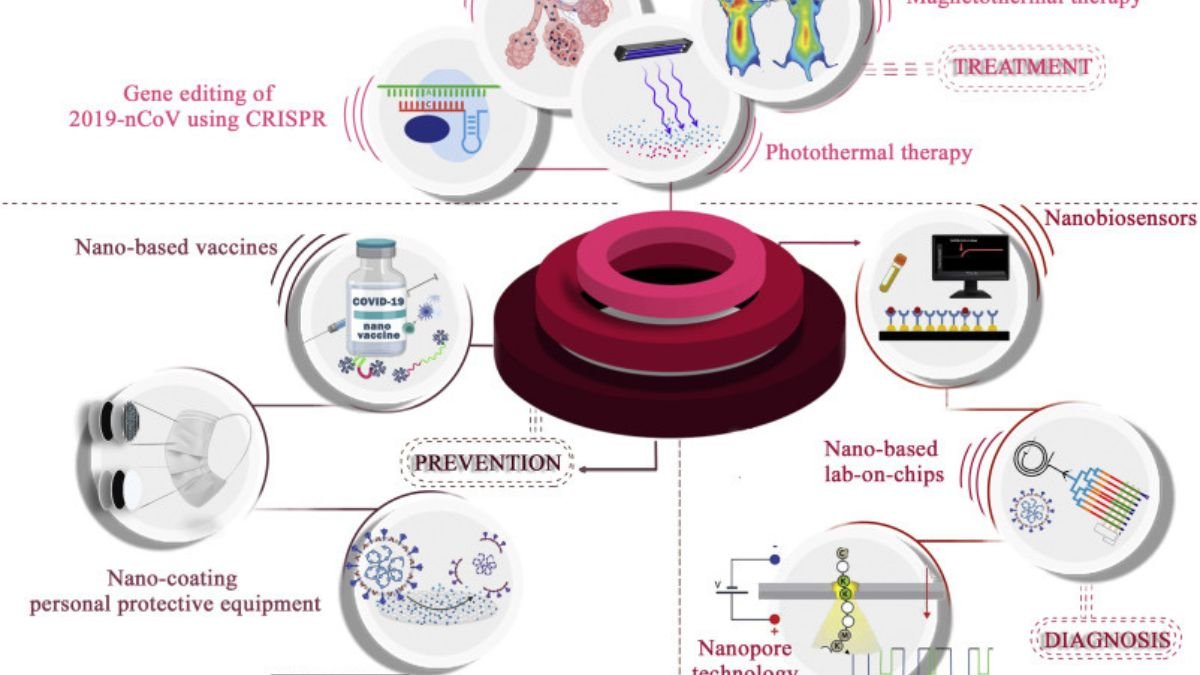
The COVID-19 pandemic tested the limits of healthcare systems, scientific research, and medical technologies worldwide. This global crisis shaped the medical world, giving rise to new branches of modern science that transcended traditional treatments. One of these was nanomedicine—the use of nanotechnology to diagnose, prevent, and treat diseases. During COVID-19, this field demonstrated promising potential that could transform future pandemic management strategies.
What is nanomedicine?
Nanomedicine is a field of science that uses nanotechnology to deliver drugs to specific parts of the body, identify viruses, and make vaccines more effective. “Nano” refers to extremely small particles—one billionth of a meter in size. These tiny particles allow scientists to design drugs to only target infected cells, increasing their effectiveness and reducing side effects.
The Role of Nanomedicine in the COVID-19 Pandemic
When the coronavirus swept the world in 2020, scientists faced a major challenge: stopping the rapid spread of the virus and developing a safe, effective vaccine. Nanomedicine played a crucial role in this effort. For example, lipid nanoparticles were used to safely deliver mRNA vaccines (such as those from Pfizer and Moderna). These nanoparticles protect the mRNA and transport it into cells, enabling the body to produce antibodies against the virus.
The Success of Nanotechnology in Vaccine Development
The success of the COVID-19 vaccine is proof that nanomedicine has opened a new chapter in medical history. Traditional vaccine technologies took years, but nanotechnology-based vaccines worked in record time. These nanoparticles not only made the vaccine more stable but also generated a faster immune response. The flexibility of this technology also suggests that vaccines can be quickly modified against new variants or other viruses in the future.
Drug Delivery and Effectiveness
A major contribution of nanomedicine has been targeted drug delivery. Lung inflammation and oxygen deficiency were the primary causes of severe COVID-19 cases. Nanoparticles made it possible to deliver drugs directly to lung cells, increasing their effectiveness and reducing side effects. This approach could also prove effective in the future for treating other respiratory diseases such as SARS, MERS, and TB.
Nanotechnology in Virus Identification and Diagnostic Testing
Nanomedicine has also revolutionized COVID-19 testing. Nano-based sensors and biomarker technologies have allowed the presence of the virus to be detected within minutes. While traditional RT-PCR tests took hours, nanosensor-based technology provided accurate results within minutes. This fast and effective testing technology proved a boon for large-scale testing during the pandemic.
Safety and Stability Challenges
Although nanomedicine has achieved many achievements, it also faces several challenges. Chief among these concerns safety and stability. Because nanoparticles are extremely tiny, their behavior in the body differs from that of conventional medicines. Scientists had to ensure that these particles did not cause toxicity. Furthermore, large-scale production and storage of nano-based vaccines or medicines was also a challenge, as their stability depends on temperature.
Scientific Lessons from COVID-19
COVID-19 taught that investment and collaboration in science are essential to combat future pandemics. Nanomedicine demonstrated that modern technology can rapidly achieve not only treatment but also prevention. The collaboration between international scientists, research institutions, and pharmaceutical companies during this pandemic proved that when technology and science work together, solutions to global crises are possible.
Future Directions: The Prospects of Nanomedicine
Now that nanomedicine has proven its effectiveness against COVID-19, scientists are working to apply it to other diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. “Smart nanoparticles” are being developed that activate automatically upon sensing specific biochemical signals in the body. This will improve both the accuracy of medications and patient recovery time.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has taught humanity many lessons—the biggest being that science and innovation can be life-saving in times of crisis. Nanomedicine is a prime example, revolutionizing vaccine development, drug delivery, and virus detection. This experience will serve as a guiding light for the medical world for decades to come.