The world is rapidly advancing technologically, and medical science is no exception. Treatments that once seemed impossible—such as the reconstruction of damaged organs or the regeneration of cells—are now becoming a reality with the help of science. At the heart of this transformation is a remarkable technology—nanomedicine.
Nanomedicine is a medical technology that operates at the nanoscale (10⁻⁹ meters). This technology utilizes nanoparticles that can directly interact with human cells and activate repair or regeneration processes in the body.
Let’s explore how nanomedicine has played a revolutionary role in the field of Regenerative Medicine.
What is Regenerative Medicine?
The goal of regenerative medicine is to regenerate or repair damaged tissues, organs, or cells in the body.
The aim of this medical approach is not just to treat the disease, but to enable the body to heal itself.
- For example: Regenerating damaged heart muscle tissue in heart disease
- Regrowing nerve cells after a spinal cord injury
- Reconstructing skin after burns or injuries
- All these treatments utilize stem cells, which are capable of generating new cells.
But delivering these stem cells to the right place, in the right amount, and at the right time is a challenge
and this is where nanomedicine has made a significant impact.
How does Nanomedicine help?
Nanomedicine plays three major roles in regenerative medicine:
- Targeted Delivery: Nanoparticles can be designed to deliver drugs, growth factors, or genes directly to the site where cells are damaged.
For example, if a person has damaged heart tissue after a heart attack, nanomedicine can deliver medication to that area to promote cell growth. - Cell Protection: When stem cells are injected into the body, they sometimes die due to the environment. Nanomedicine provides them with a protective “shell,” increasing their viability.
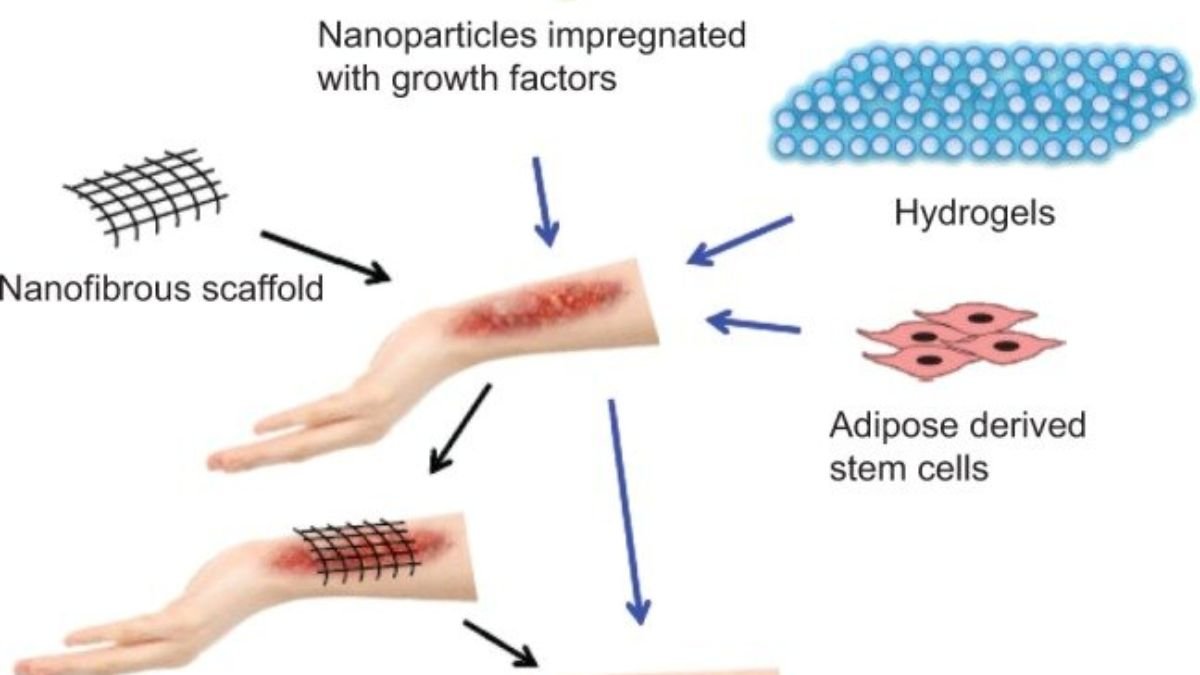
- Nano-Scaffolds: These are artificial structures that help cells in the body to attach, grow, and form new tissue.
Scientists create these scaffolds using nanofiber technology, which provides a texture similar to human tissues.
Nanomedicine in Heart and Brain Diseases
The heart and brain are two organs whose cells do not regenerate.
But with the help of nanomedicine, this limitation is now being challenged.
- Heart Disease: Cardiac nanoparticles precisely deliver drugs or proteins to heart tissue.
This leads to the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) and the regeneration of damaged muscles. - Brain Disorders: The blood-brain barrier is a major obstacle that prevents drugs from reaching the brain.
But nanoparticles are so small that they can cross this barrier and deliver therapeutic materials to brain cells.
Role in Skin and Bone Regeneration
Nanomedicine has also shown remarkable performance in skin tissue engineering and bone regeneration.
In Skin Regeneration: Nanofiber scaffolds are being used to promote the growth of new skin after burns or injuries.
These scaffolds gradually dissolve in the body and promote the formation of new cells.
In Bone Repair: Nanoparticles contain minerals such as calcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite, which are essential for bone strength.
They are applied to damaged bone areas, leading to faster formation of new bone.
The Combination of Stem Cells and Nanomedicine
- Stem cells are amazing in themselves, but when combined with nanomedicine, the results are miraculous.
- Nanomedicine not only protects stem cells but also “guides” them—telling them which direction to move in and which cells to transform into.
- For example, in bone regeneration, nanoparticles send chemical signals that cause stem cells to differentiate into “osteoblasts,” or bone-forming cells.
Global Research and Japan’s Progress
- Countries like Japan, the USA, and South Korea are leaders in this field.
- Institutions such as the University of Tokyo, the RIKEN Institute, and the Osaka Medical Center are conducting extensive research on biocompatible nanoparticles and nanoscaffolds.
- Japan recently developed a “smart nanoparticle system” that can not only identify damaged tissue but also release medication as needed.
- This automated and intelligent system could prove to be the next big leap in regenerative medicine.
Challenges of Nanomedicine
However, this technology is as challenging as it is fascinating.
- Safety: Some nanoparticles may contain toxic elements (such as cadmium), which can accumulate in the body and cause harm.
- Cost: Nanotechnology-based treatments are still expensive, making them inaccessible to the general public.
- Clinical Approval: Many experiments are still at the laboratory stage. Long-term trials are needed before they can be used in widespread medical applications.
Future Possibilities
In the future, nanomedicine is poised to become the most powerful tool in the medical world.
Its combination with AI and bioengineering could be the first step towards a self-healing body system
where the body can recognize, repair, and protect itself from diseases Scientists believe that in the next decade, nanomedicine will play a crucial role in areas such as artificial organ manufacturing, neural repair, and aging reversal.
Conclusion
Nanomedicine is not just a scientific invention, but the future of human health It has redefined regenerative medicine where treatment means not just medication, but activating the body’s own healing power What is a subject of research in laboratories today could become a common treatment in our hospitals tomorrow.
If this technology is made safe and accessible, it could be a lifesaver for millions of people who are currently struggling with permanent injuries, diseases, or disabilities.